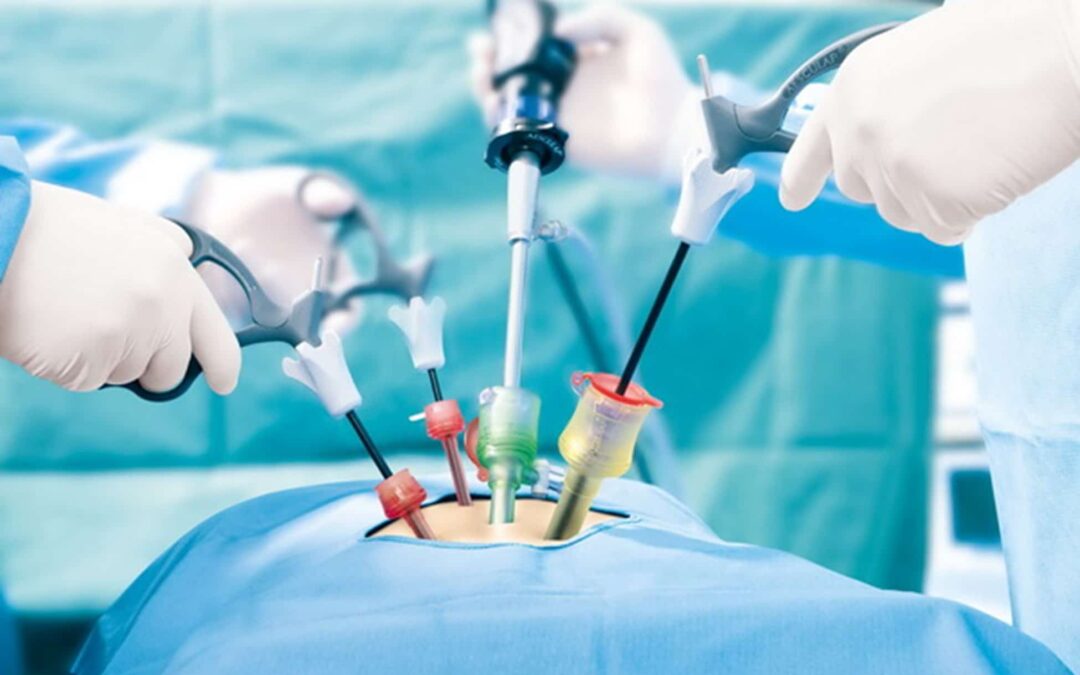
Laparoscopy is a modern surgical technique that allows doctors to diagnose and treat conditions inside the abdomen and pelvis through very small incisions, using a special camera (laparoscope). It’s often referred to as “keyhole surgery.”
1. Advantages Over Traditional Surgery
- Minimally Invasive – Requires tiny cuts instead of a large incision, reducing trauma to the body.
- Less Pain – Smaller wounds cause less post-operative discomfort.
- Faster Recovery – Patients often go home sooner and return to normal activities quicker.
- Lower Risk of Infection – Small openings reduce the exposure of internal tissues.
- Better Cosmetic Results – Minimal scarring compared to open surgery.
2. Common Uses
- Diagnostic Purposes – To investigate causes of abdominal or pelvic pain, infertility, or unexplained symptoms.
- Surgical Treatment – For removing the gallbladder (laparoscopic cholecystectomy), appendix, ovarian cysts, fibroids, hernias, or even for bariatric surgery.
- Cancer Staging – Helps assess how far certain cancers have spread.
3. How It Works
- Small Incisions are made in the abdominal wall.
- CO₂ Gas Inflation creates space to work and improves visibility.
- Laparoscope Insertion (camera with light) allows real-time video guidance on a monitor.
- Special Instruments are used to perform the procedure.
- Closure with minimal stitches or surgical glue.
4. Risks and Limitations
- Possible Complications – Bleeding, infection, injury to nearby organs.
- Anesthesia Risks – As with any surgery under general anesthesia.
- Conversion to Open Surgery – If complications or visibility issues occur.
- Not Suitable for All Patients – For example, those with severe heart or lung problems or extensive abdominal adhesions.
5. Why It’s Preferred in Modern Medicine
- It combines high precision, quicker healing, and better patient comfort, making it the go-to choice for many surgical conditions.
- Hospitals often choose laparoscopy when safe and feasible because it improves both patient outcomes and hospital efficiency.